Bypass (medicine)
A bypass is a surgical procedure that creates an alternative pathway or bridge. It involves bypassing a normal anatomical structure and redirecting flow through a new pathway.
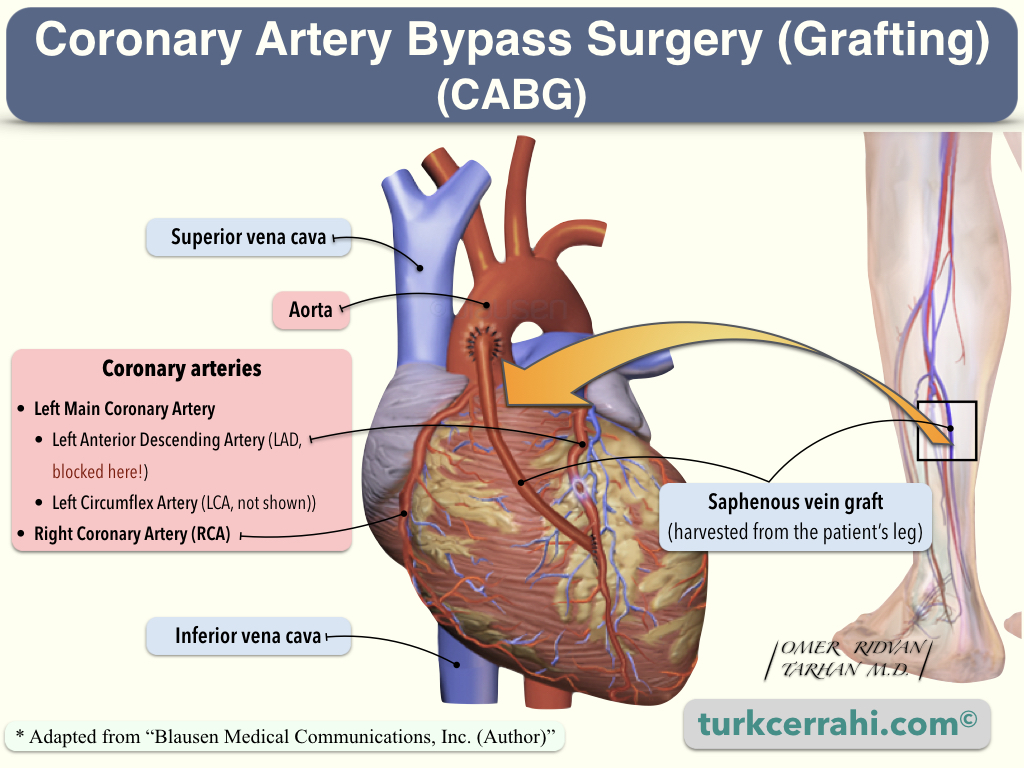
Image retrieved from Wikipedia on 29 June 2023 under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported. By Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. (Author). Image’s Page
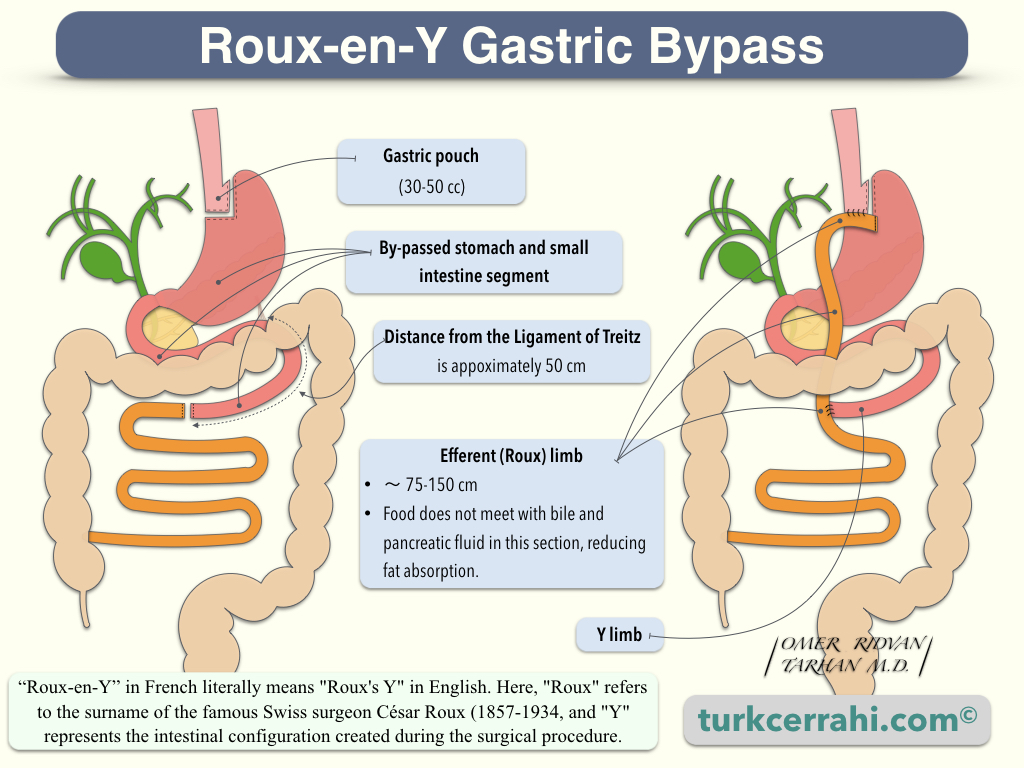
Examples
- Coronary artery bypass surgery is a type of vascular bypass surgery. A vessel is sewn around the blocked portion of the heart artery (coronary artery) so that blood can flow around the blockage. One end of the vessel is sewn before the blockage, and the other end is sewn after the blockage. This new vessel then becomes the pathway for blood flow, bypassing the blocked (obstructed) artery.
- Cardiopulmonary bypass is a method used in open-heart surgery. All blood entering the heart (from the body) is redirected to a heart-lung machine through plastic tubes. The heart-lung machine oxygenates the blood before it is pumped back to the body through the outgoing blood vessels of the heart. This allows the heart to be stopped temporarily during surgical procedures such as bypassing a blocked artery, replacing a valve, removing a tumor, etc.
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery is a form of bariatric surgery used to treat obesity. In this procedure, a large portion of the stomach and a segment of the small intestine (usually 100-150 cm) are bypassed or redirected. This restricts the amount of food that the body can absorb.
- Ileal bypass surgery is also a form of bariatric surgery that involves bypassing a portion of the small intestine in order to reduce the amount of food absorbed by the body.
- Ileojejunal bypass surgery is another form of bariatric surgery that involves bypassing a portion of the small intestine to reduce the amount of food absorbed by the body.